
Python Data Science Handbook: Essential Tools for Working with Data. Pandas for Everyone : Python Data Analysis. Hands-On Data Analysis with Pandas: Efficiently perform data collection, wrangling, analysis, and visualization using Python. Python for Data Analysis : Data Wrangling with Pandas, NumPy, and IPython (2nd ed.). ^ "NumFOCUS – pandas: a fiscally sponsored project".^ "Indexing and selecting data - pandas 1.4.1 documentation".^ "Reshaping and pivot tables - pandas 1.4.1 documentation".^ "Merge, join, concatenate and compare - pandas 1.4.1 documentation".^ "IO tools (Text, CSV, HDF5, …) - pandas 1.4.1 documentation".
"Meet the man behind the most important tool in data science". Python for Data Analysis, Second Edition. "pandas: a Foundational Python Library for Data Analysis and Statistics" (PDF). ^ "License – Package overview – pandas 1.0.0 documentation".
#Python pandas series
dataframes, multidimensional time series and cross-sectional datasets commonly found in. "Introduction to Python Pandas for Beginners". Pandas is a Python library for data manipulation and analysis, e.g. In 2015, pandas signed on as a fiscally sponsored project of NumFOCUS, a 501(c)(3) nonprofit charity in the United States. Before leaving AQR he was able to convince management to allow him to open source the library.Īnother AQR employee, Chang She, joined the effort in 2012 as the second major contributor to the library. The pandas library is built upon another library NumPy, which is oriented to efficiently working with arrays instead of the features of working on DataFrames.ĭeveloper Wes McKinney started working on pandas in 2008 while at AQR Capital Management out of the need for a high performance, flexible tool to perform quantitative analysis on financial data. The development of pandas introduced into Python many comparable features of working with DataFrames that were established in the R programming language. Pandas allows various data manipulation operations such as merging, reshaping, selecting, as well as data cleaning, and data wrangling features. Pandas allows importing data from various file formats such as comma-separated values, JSON, Parquet, SQL database tables or queries, and Microsoft Excel. Pandas is mainly used for data analysis and associated manipulation of tabular data in DataFrames. Wes McKinney started building what would become pandas at AQR Capital while he was a researcher there from 2007 to 2010. Its name is a play on the phrase "Python data analysis" itself. The name is derived from the term " panel data", an econometrics term for data sets that include observations over multiple time periods for the same individuals.
#Python pandas software
It is free software released under the three-clause BSD license. In particular, it offers data structures and operations for manipulating numerical tables and time series. On the contrary, DataFrame API heavily relies on the parameter, because it’s a two-dimensional data structure, and many operations can be performed along different axes producing totally different results.Pandas is a software library written for the Python programming language for data manipulation and analysis. The “axis” parameter does not have any influence on a Series object because it has only one axis. Pandas borrowed the “axis” concept from NumPy library.
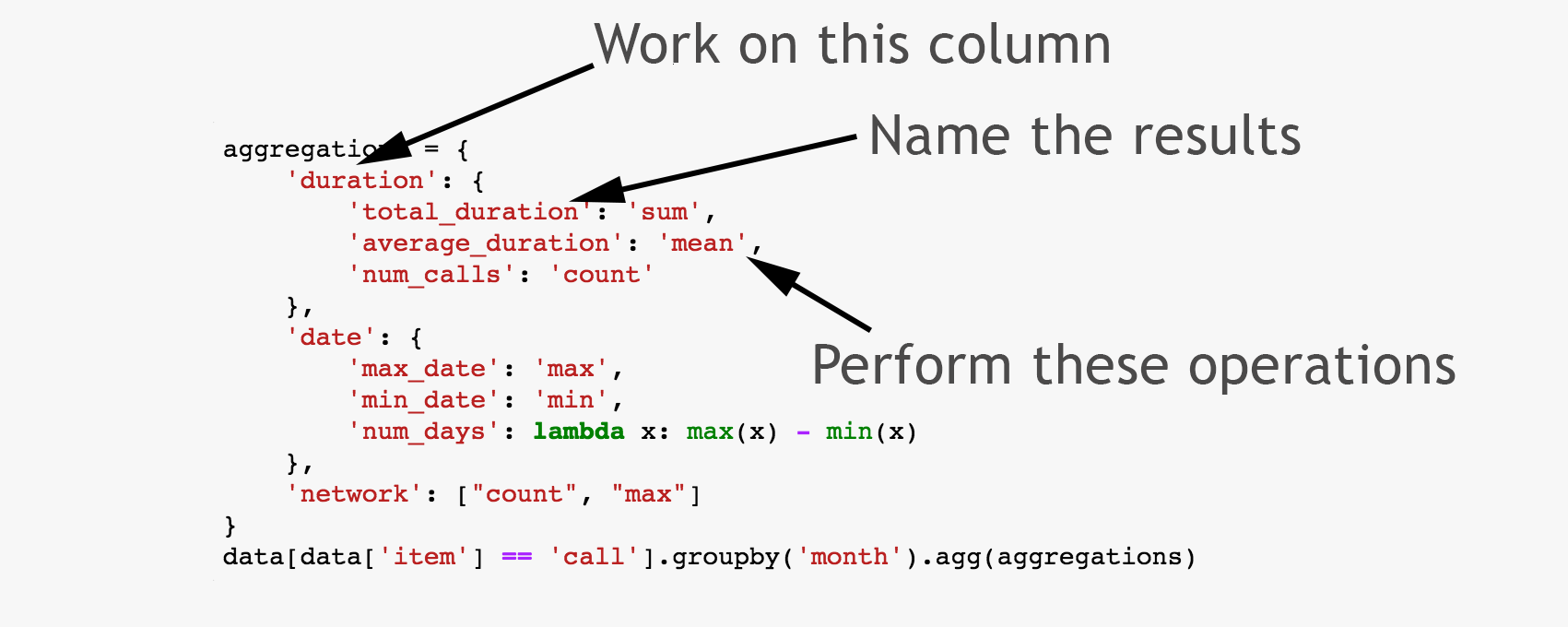
With axis=1 both DataFrames are put along each other: > pd.concat(, axis=1) Also, instead of bare brackets, we need to use. To access an element within DataFrame we need to provide two indexes (one per each axis). Our DataFrame object has 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 indexes along the “axis 0”, and additionally, it has “axis 1” indexes which are: ‘a’ and ‘b’. In this guide, you’ll learn about the pandas library in Python The library allows you to work with tabular data in a familiar and approachable format. Now it’s clear that Series and DataFrame share the same direction for “axis 0” – it goes along rows direction. “axis 0” represents rows and “axis 1” represents columns. Let’s see an example:Ī DataFrame object has two axes: “axis 0” and “axis 1”.
Its columns are made of separate Series objects. > srs = pd.Series()ĭataFrame is a two-dimensional data structure akin to SQL table or Excel spreadsheet. Here is an example of accessing different values: > import pandas as pd For our Series object indexes are: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4. On the contrary, here we see that Series is displayed as a column of values.Įach cell in Series is accessible via index value along the “axis 0”. Usually, in Python, one-dimensional structures are displayed as a row of values.
The arrow on the image displays “axis 0” and its direction for the Series object. Series object has only “axis 0” because it has only one dimension. NumPy uses it quite frequently because ndarray can have a lot of dimensions. Series is a one-dimensional array of values.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
